This is an old revision of the document!
Model state
Definition 1. A state of a model $\mathbf{A} = (D, B, \alpha^0)$, where $D = (A, C, \sigma)$ and $A = \{X_1,...,X_n\}$ is a tuple
$$S = (S(X_1),\dots,S(X_n)).$$
Definition 2. The initial state is defined as follows:
- $am(X) = \mathsf{X}$, for any active agent $X$ such that $\sigma(X) = \mathit{True}$.
- $am(X) = \mathsf{I}$, for any active agent $X$ such that $\sigma(X) = \mathit{False}$.
- $am(X) = \mathsf{W}$, for any passive agent $X$.
- $pc(X) = 1$ for any active agent $X$ in the running mode and $pc(X) = 0$ for other agents.
- $ci(X) = [\; ]$ for any active agent $X$.
- $ci(X)$ contains names of all accessible procedures of $X$ together with the direction of parameters transfer, e.g. $in(a)$, $out(b)$, etc. for any passive agent $X$.
- For any agent $X$, $pv(X)$ contains $X$ parameters with their initial values.
Example: Sender-Buffer-Receiver system
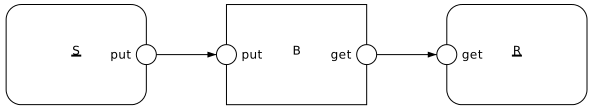
agent Sender {
loop { -- 1 comments contain steps numbers
out put; -- 2
}
}
agent Buffer {
i :: Int = 0;
proc (i == 0) put {
in put; -- 1
i = 1; -- 2
}
proc (i /= 0) get {
out get; -- 3
i = 0; -- 4
}
}
agent Receiver {
loop { -- 1
in get; -- 2
}
}
Initial state:
S_0 = ((X,1,[],()), (W,0,[in(put)],(0)), (X,1,[],()))
See also: Sender-Buffer-Receiver example
